 |
CIRPASS Demonstration Science Results
|
CIRPASS, the near-infrared integral field unit (IFU) spectrograph constructed
by the Institute of Astronomy (University of Cambridge), recently completed a
very successful 9-night Demonstration Science run on Gemini South under the
leadership of Ian Parry and Andrew Bunker (IoA). This
represents the first use of a near-IR IFU on an 8m-class telescope.
A number of science programs were conducted:
- 2D mapping the of the velocity structure emission line gas in the z=1.2 radio galaxy
3C324 (previously also observed with the GMOS IFU)
- A study of star formation and kinematics in two z=1 galaxies using H-alpha
- A deep survey of damped Lyman-alpha systems: two targets at z=1.5 at H-alpha, one at z=3
at [OII] (also previously observed with GMOS searching for Ly-alpha). It is
expected that after complete processing these data will produce a detection or the strongest limits to date on star formation in these systems.
- A high signal-to-noise study of the Einstein cross q2237+03 (a lensed QSO at z=1.7), comparing the narrow and broad line components
in the four images to investigate "clumping" in the dark matter distribution of the foreground lensing galaxy.
- A spatially-resolved study of a giant lensed arc at z=1.6 in [OII] and H-beta emission.
- An investigation of young star clusters in NGC1140 to measure
the ages of several clusters in the central starburst region.
- Measurement of velocity dispersions of Galactic star clusters (including M30, the quintuplet cluster,
and around Sgr-A).
- During commissioning, observations of several bright targets were made for
system characterisation and calibrations, including: a partial map of the Eagle nebula
in multiple emission lines, the planetary nebula NGC6369, the planet Uranus,
and the SN1987a shells in Paschen-alpha.
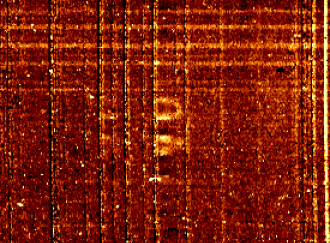 |
The example data shown left is from the z=1.2
radio galaxy 3C324. (Dispersion runs horizontally, spatial direction
is vertical; each of the 500 IFU lenslets produces a spectrum 2 pixels
high).
The preliminary processing (basic sky subtraction and cosmic ray
rejection) of this single 20 minute exposure shows a very clear detection
of the [OIII]500.7nm emission line (centre of the frame).
More data on 3C324 and the other science programs can be found at the IoA
CIRPASS results page. |
As with all Gemini Demonstration Science data, it is intended that these
datasets will be made publicly available within 2 months. Further details will
be provided at that time.
![[Science Operations home]](../../generic-images/sciopshomebtn.gif)
Last update 15 August 2002; Phil Puxley


