Resolving the Hearts of Luminous Infrared Galaxies
October 30, 2006

An international team of researchers used Gemini mid-infrared images to investigate a sample of nearby Luminous InfraRed Galaxies (LIRGs) which are analogous to those LIRGs which are major contributors to the obscured star formation rate (SFR) density at redshift z=1, when the universe was half of its present age.
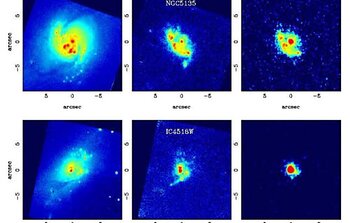
The data were obtained with the mid-infrared imager/spectrograph T-ReCS on Gemini South. In Figure 1 the diffraction-limited images reveal that at high-spatial resolution, approximately 0.3 arcsecond at the observed wavelengths of 8 and 10 microns, the morphology of the mid-infrared emission in the nuclear regions of these galaxies is strikingly similar to that of the ionized gas (Paschen-alpha) revealed by Hubble Space Telescope (HST) NICMOS observations at near-infrared wavelengths. The observed mid-infrared emission of these LIRGs generally consists of bright nuclear emission, multiple circumnuclear and/or extranuclear H II regions, and diffuse emission. The stellar emission, traced by the NICMOS near-infrared continuum images, is more extended and does not show such a close resemblance with the hot dust emission traced by the T-ReCS images.
These new data lead to the conclusion that calibration of the SFR for distant galaxies should be based on the integrated mid-infrared flux, not that of the H II regions alone. This study also illustrates the need for high-spatial resolution imaging since it is often necessary to separate emission components to arrive at a more precise understanding of the underlying physical processes.
The team includes Almudena Alonso-Herrero (Departamento de Astrofísica Molecular e Infrarroja, DAMIR, Instituto de Estructura de la Materia (IEM),CSIC, Spain), Chris Packham (University of Florida), Luis Colina (DAMIR, IEM, CSIC, Spain), Tanio Diaz-Santos (DAMIR, IEM, CSIC, Spain), George Rieke (University of Arizona), James Radomski (Gemini Observatory), and Charles Telesco (University of Florida).
See more details in the paper "High Spatial Resolution T-ReCS mid-infrared imaging of Luminous Infrared Galaxies" by Alonso-Herrero et al., The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2006, in press (astro-ph/0610394)